Parallel port (EEG triggers)
In EEG/ ERP studies it is common to send triggers to mark the timestamp for significant events (e.g., the onset of a trial, presentation of a particular stimulus, etc.). Triggers are typically bytes that are sent via the parallel port to the EEG apparatus.
Using the parallel_port_trigger plugin
Parallel_port_trigger is a third-party plugin, but has been reviewed by the OpenSesame team.
Triggers can be sent with the parallel_port_trigger plugin which works under Linux and Windows.
The plugin has three input boxes:
- The value ranges between 0-255 and specifies the trigger byte.
- The duration (in ms) is the time that the trigger is on. Unless a 0 ms duration was specified, the trigger will be reset to 0 after this interval.
- The port address has to be specified manually. This setting applies only to Windows and is ignored under Linux.
You can download the plugin from here:
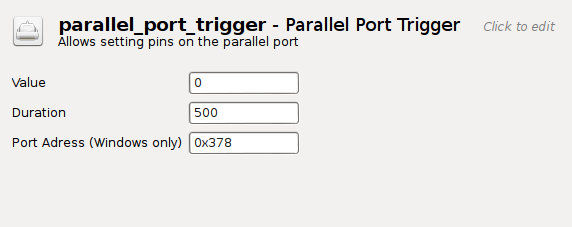
Figure 1. A screenshot of the parallel_port_trigger plugin.
Using dportio.dll in a Python inline Script (Windows only)
Instead of using the parallel_port_trigger plugin, it is also possible to send triggers with dlportio.dll through a Python inline script. This approach is Windows only. To do so, first add an inline_script to the start of the experiment with the following code in the prepare phase:
try:
from ctypes import windll
global io
io = windll.dlportio # requires dlportio.dll !!!
except:
print 'The parallel port couldn\'t be opened'
This will load dlportio.dll as a global object called io. Please note that failure will not crash the experiment, so make sure to check the debug window for error messages!
Now use the following code in an inline_script anywhere in the experiment to send a trigger:
global io
trigger = 1
port = 0x378
try:
io.DlPortWritePortUchar(port, trigger)
except:
print 'Failed to send trigger!'
Note that this sends trigger 1 to port 0x378 (=888). Change these values according to your set-up.
Getting access to the parallel port
Linux
In Linux we use the parport_pc module (tested in Debian Wheezy) and we need to provide ourselves with permissions to do so. We can accomplish this by executing the following commands:
sudo rmmod lp
sudo rmmod parport_pc
sudo modprobe parport_pc
sudo adduser [user] lp
Here, [user] should be replaced by your username. Next, logout and login, and you are ready to go!
Windows XP and Windows Vista (32 bit)
- Download the 32-bit DLPortIO driver from here and uncompress the zip archive.
- Go to
DriverLINX/driversfolder and copydlportio.dllanddlportio.systo theinstallfolder. This is the folder whereinstall.exeis located. Then runinstall.exe - You need to copy
dlportio.dllto the OpenSesame folder (that is, the same folder that containsopensesame.exe).
Windows 7 (32 and 64 bit)
- Download the 32-bit or 64bit DLPortIO driver here and uncompress the zip archive.
- As Windows 7 has a strengthened security system (at least compared to XP) one cannot simply install the DLPortIO driver. This won't work as Windows 7 will block all attempts of installing a not-officially-signed (by Microsoft) driver. Good for the security of an average user -- bad for us. To bypass this restriction one has to use a little helper program called "Digital Signature Enforcement Overrider" (DSEO) which can be downloaded here (of course there are other possible ways to do this but this program is mentioned in the DLPortIO
readme.txtand one does not have to dive deeper into MS Windows 7 architecture specialities). - Start DSEO with administrator privileges (right click on
dseo13b.exe, select "run as administrator"). Now the DSEO window pops up. It just presents a list of options which operation to run next. - Choose the option "sign driver/sys-file" and press ok. Now another window appears where you have to type in the absolute path to the
DLPortIO.sysfile (only this one, not the dll!). Remember to escape spaces in the path if you have any (don't ask how long that took me) otherwise your files will not be found. Pressing ok will sign the sys-file. - Back in the DSEO list choose "enable test mode" and press ok. Then choose "exit" and restart your PC. Windows 7 wrongly complains that DSEO might not be installed correctly -- just click on "yes, the software is installed correctly".
- After boot-up is completed you'll see that something like "Windows 7 test mode built #number#" is written on the desktop just above the clock in the starter-bar. That's necessary. You have to be in test mode to run this unofficially signed driver.
- Now run
DLPortIO_install.batwith administrator privileges (in Windows Explorer, right click the file, ...). Answer "yes" if Windows warns you about registry changes. - Reboot.
- Copy
DLPortIO.dllto the Opensesame folder, that is, the same folder that containsopensesame.exe.
Source: Forum post by Absurd
Recommendations
- Start your experiment with a 'zero' trigger to make sure all the pins are set to zero.
- It's recommended to use the psycho or xpyriment backends instead of the legacy backend (using PyGame) for time-critical experiments. This is because psycho and xpyriment takes the refresh rate of the monitor into account when returning timestamps, whereas legacy does not. For more information, see miscellaneous/timing.
- Send the trigger code right after (instead of just before) the presentation of your stimulus (assuming that it's the stimulus onset you want to mark). By doing so you'll make sure that the time stamp is as accurately as possible and will not suffer from a small random jitter due to your monitor's refresh rate. Source: lvanderlinden
Troubleshooting
There are a number of relevant forum topics in which trigger-related problems are discussed (and, for the most, solved!).
- A post about ghost triggers, i.e. unwanted triggers that are mysteriously registered by the EEG apparatus: link
- A post with elaborate installation instructions for DLPortIO on Windows 7 (Source: absurd).
Please don't hesitate to post questions on the forum, or to let us know of your experiences (good or bad).





